Colorless transparent liquid;
CAS no. 79-10-7;
Soluble in water, ethanol,ether;
Corrosive to metals, tissue.
| Chemical Identification |
|
Common Name: |
Acrylic acid |
|
|
2-propenoic acid; Acroleic acid; Acrylic acid; Ethylenecarboxylic acid; Monoethylene carboxylic acid; Propenoic acid; |
|
CAS No.: |
79-10-7 |
|
EINECS No.: |
201-177-9 |
|
Appearance: |
Colorless transparent liquid |
|
Density: |
1.051 |
|
Flash Point: |
54.5ºC |
|
Melting Point: |
13ºC |
|
Boiling Point: |
141.3ºC |
|
Stability: |
Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, amines. |
|
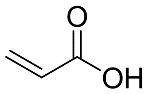
Molecular Formula: |
C3H4O2 |
|
Molecular Weight: |
72.06 |
|
|
|
| Product Information |
Specifications:
|
Product name: Glacial Acrylic Acid Manufacturer: Ningbo Titan Unichem Co., Ltd. |
|
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Appearance |
Clear colorless liquid |
|
Purity |
99.5% min. |
|
Color (PT-CO) |
15 max |
|
Furfural |
2.0 ppm max. |
|
Water Content |
0.15% max |
|
Inhibitor Content (MEHQ) |
180-220 ppm |
Pictures:

Loading of Acrylic acid from TITAN UNICHEM.

Loading of Acrylic acid from TITAN UNICHEM.

Loading of Acrylic acid from TITAN UNICHEM.
Packaging:
-
Packed in 200kg HDPE drum (16mt/20'GP), ISO tank (20mt +/- 5%);
-
Or package as per customer's request.
Delivery:
-
Prompt shipment within 2 weeks.
Storage & Handling:
-
Keep container dry.
-
Keep container tightly closed, in a cool, well-ventilated area.
-
Keep away from extreme heat and oxidizing agents.
Safety Information:
|
Hazard Class: |
8 |
|
RIDADR: |
UN 2218 |
|
Packing Group: |
II |
|
HS Code: |
2916110000 |
|
Risk Statements: |
R10; R20/21/22; R35; R50 |
|
Safety Statements: |
S26-S36/37/39-S45-S61 |
|
Hazard Codes: |
C: Corrosive |
| Application |
Descriptions:
-
Acrylic acid is a colorless liquid with a distinctive acrid odor.
-
It's corrosive to metals and tissue.
-
Prolonged exposure to fire or heat can cause polymerization.
-
If polymerization takes place in a closed container, violent rupture may occur.
-
The inhibitor (usually hydroquinone) greatly reduces the tendency to polymerize.
Uses:
-
Used to produce copolymerization monomer butyl acrylate, ethyl ester and other esters, which mostly used in water soluble coatings, adhesives, thickeners, super absorbent compounds,etc.
-
Used in coating acrylic products, building materials, textile, cement, paper making, leather processing and plastic modification industry,etc.
-
Glacial Acrylic Acids is mostly used in the production of super absorbent resin. Mainly include health supplies, soil improvement, water retention agent, medical material, chemical and oil additives, deodorant, balmy agent, etc.
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|


















